By Seung Ha Son, Yong Nam In, MD, Jung Soo Park, Yeonho You, Jin Hong Min, Insool Yoo, Yong Chul Cho, Wonjoon Jeong, Hong Joon Ahn, Changshin Kang & Byung Kook Lee
First Online: 11 January 2021
Background/Objective
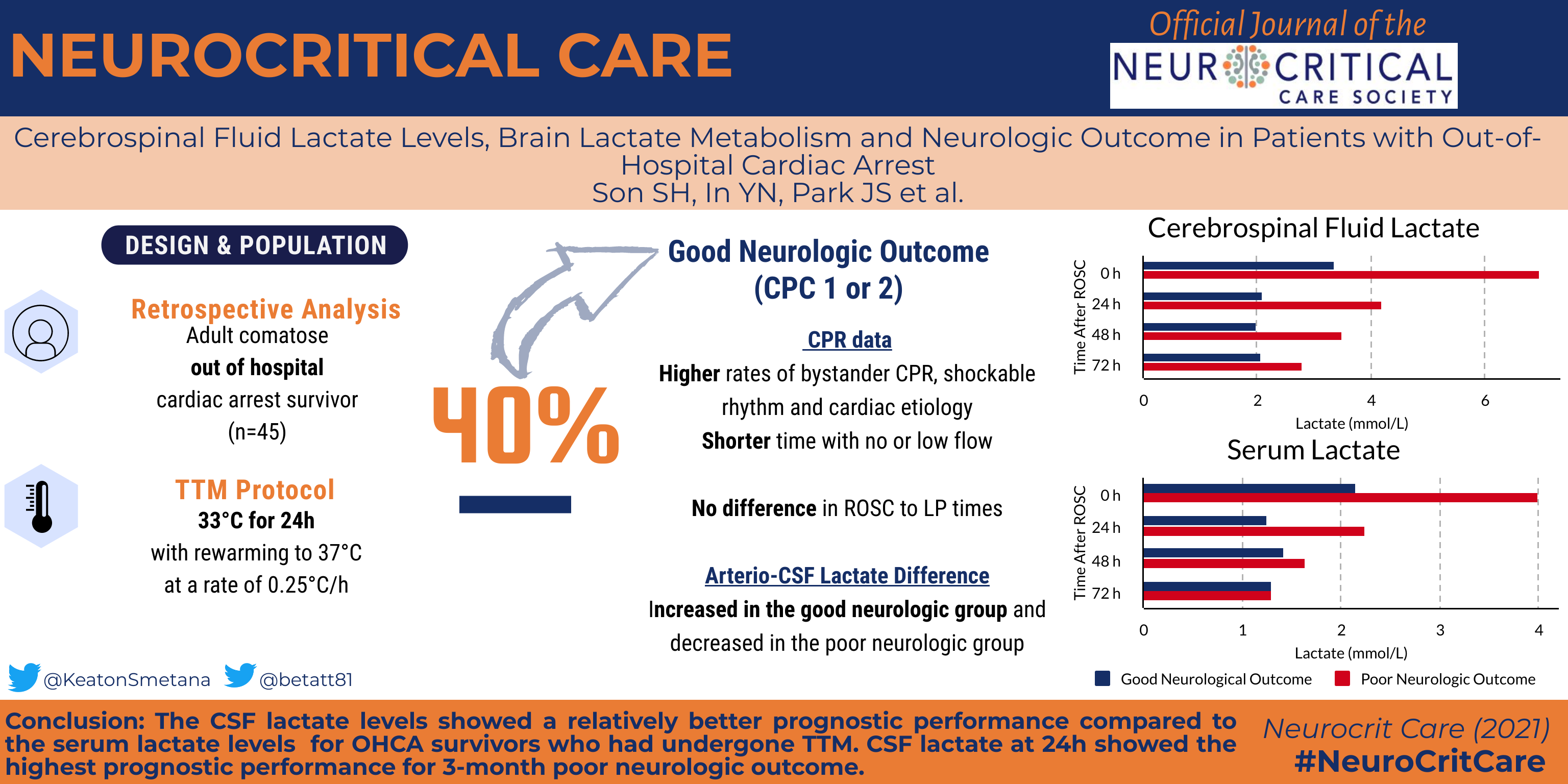
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum lactate levels were assessed to predict poor neurologic outcome 3 months after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). We compared arterio-CSF differences in the lactate (ACDL) levels between two neurologic outcome groups.
Methods
This retrospective observational study involved out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) survivors who had undergone target temperature management. CSF and serum samples were obtained immediately (lactate0), and at 24 (lactate24), 48 (lactate48), and 72 (lactate72) h after ROSC, and ACDL was calculated at each time point. The primary outcome was poor 3-month neurologic outcome (cerebral performance categories 3–5).
Results
Of 45 patients, 27 (60.0%) showed poor neurologic outcome. At each time point, CSF lactate levels were significantly higher in the poor neurologic outcome group than in the good neurologic outcome group (6.97 vs. 3.37, 4.20 vs. 2.10, 3.50 vs. 2.00, and 2.79 vs. 2.06, respectively; all P < 0.05). CSF lactate’s prognostic performance was higher than serum lactate at each time point, and lactate24 showed the highest AUC values (0.89, 95% confidence interval, 0.75–0.97). Over time, ACDL decreased from − 1.30 (− 2.70–0.77) to − 1.70 (− 3.2 to − 0.57) in the poor neurologic outcome group and increased from − 1.22 (− 2.42–0.32) to − 0.64 (− 2.31–0.15) in the good neurologic outcome group.
Conclusions
At each time point, CSF lactate showed better prognostic performance than serum lactate. CSF lactate24 showed the highest prognostic performance for 3-month poor neurologic outcome. Over time, ACDL decreased in the poor neurologic outcome group and increased in the good neurologic outcome group.
Read full article here.