By: Neeraj Badjatia, Stephanie Sanchez, Gabriella Judd, Rachel Hausladen, David Hering, Melissa Motta, Gunjan Parikh, Wendy Chang, Nicholas Morris, J. Marc Simard, John Sorkin, George F. Wittenberg & Alice S. Ryan
Published: 04 November 2020
Introduction
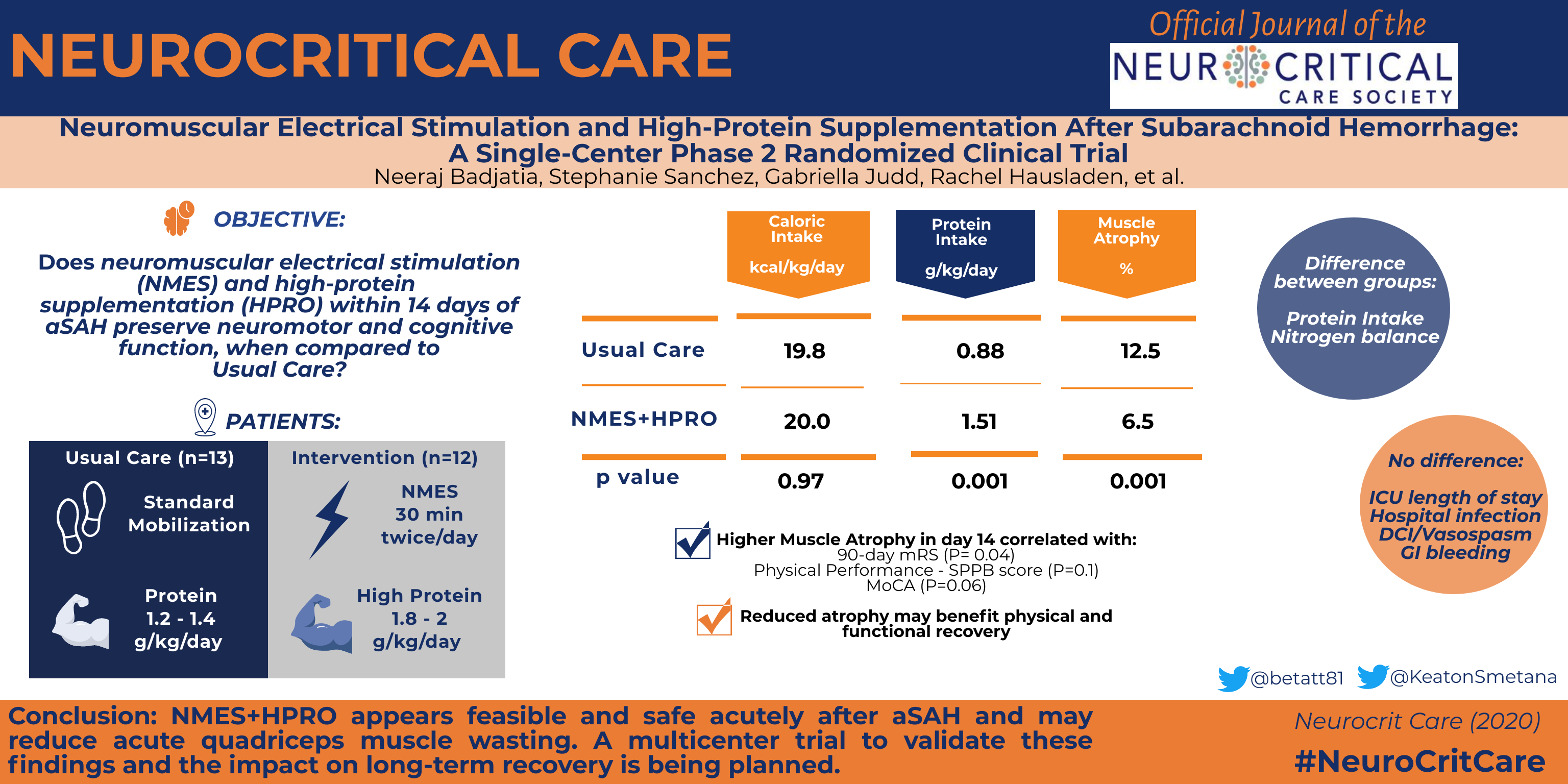
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) survivors live with long-term residual physical and cognitive disability. We studied whether neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) and high-protein supplementation (HPRO) in the first 2 weeks after SAH could preserve neuromotor and cognitive function as compared to standard of care (SOC) for nutrition and mobilization.
Methods
SAH subjects with a Hunt Hess (HH) grade > 1,modified Fisher score > 1 and BMI < 40 kg/m2 were randomly assigned to SOC or NMES + HPRO. NMES was delivered to bilateral quadricep muscles daily during two 30-min sessions along with HPRO (goal:1.8 g/kg/day) between post-bleed day (PBD) 0 and 14. Primary endpoint was atrophy in the quadricep muscle as measured by the percentage difference in the cross-sectional area from baseline to PBD14 on CT scan. All subjects underwent serial assessments of physical (short performance physical battery, SPPB) cognitive (Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale, MoCA) and global functional recovery (modified Rankin Scale, mRS) at PBD 14, 42, and 90.
Read the full article.