By Elizabeth K. Zink, Sowmya Kumble, Meghan Beier, Pravin George, Robert D. Stevens & Mona N. Bahouth
First Online: 22 March 2021
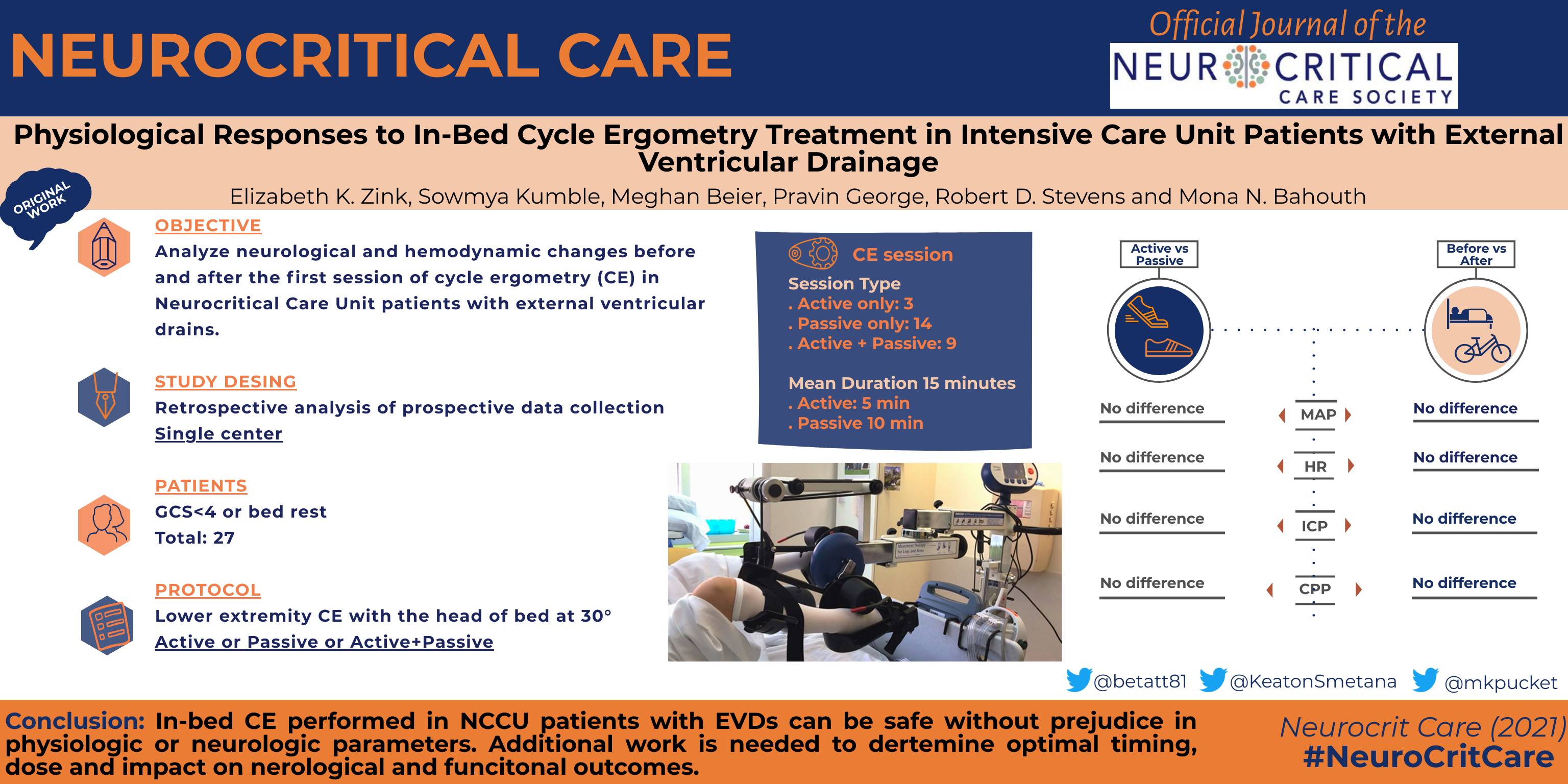
Purpose
Evidence suggests that early physical activity can be accomplished safely in the neurocritical care unit (NCCU); however, many NCCU patients are often maintained in a state of inactivity due to impaired consciousness, sensorimotor deficits, and concerns for intracranial pressure elevation or cerebral hypoperfusion in the setting of autoregulatory failure. Structured in-bed mobility interventions have been proposed to prevent sequelae of complete immobility in such patients, yet the feasibility and safety of these interventions is unknown. We studied neurological and hemodynamic changes before and after cycle ergometry (CE) in a subset of NCCU patients with external ventricular drains (EVDs).
Methods
Patients admitted to the NCCU who had an EVD placed for cerebrospinal fluid drainage and intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring underwent supine CE therapy with passive and active cycling settings. Neurologic status, ICP and hemodynamic parameters were monitored before and after each CE session.
Results
Twenty-seven patients successfully underwent in-bed CE in the NCCU. No clinically significant changes were recorded in neurologic or in physiological parameters before or after CE. There were no device dislodgements or other adverse effects requiring cessation of a CE session.
Conclusion
These data suggest that supine CE in a heterogeneous cohort of neurocritical care patients with EVDs is safe and tolerable. Larger prospective studies are needed to determine the efficacy and optimal dose and timing of supine CE in neurocritical care patients.
Read the full article here.